The true start codon is the first ATG encountered downstream of the Shine-Dalgarno sequence. How do eukaryotic transcription factors help form the initiation complex.

15 3a Initiation Of Transcription In Eukaryotes Biology Libretexts
The initiation of gene transcription in eukaryotes occurs in specific steps.

. First an RNA polymerase along with general transcription factors binds to the promoter region of the gene to form a closed complex called the preinitiation complex. How do eukaryotic transcription factors help form the initiation complex. In the absence of a TATA sequence PIC assembly is initiated by association of other subunits of TFIID with other promoter elements see below.
Formation of the transcription preinitiation complex PIC is nucleated by the TATA-binding protein TBP a subunit of TFIID that binds the TATA element and induces a sharp bend in the DNA. During this process the DNA sequence of a gene is copied into RNA. Initiation elongation and termination.
Inherent in this step are the events that determine whether or not the gene is actually expressed. Transcription is the first step of gene expression. The human body contains many transcription factors.
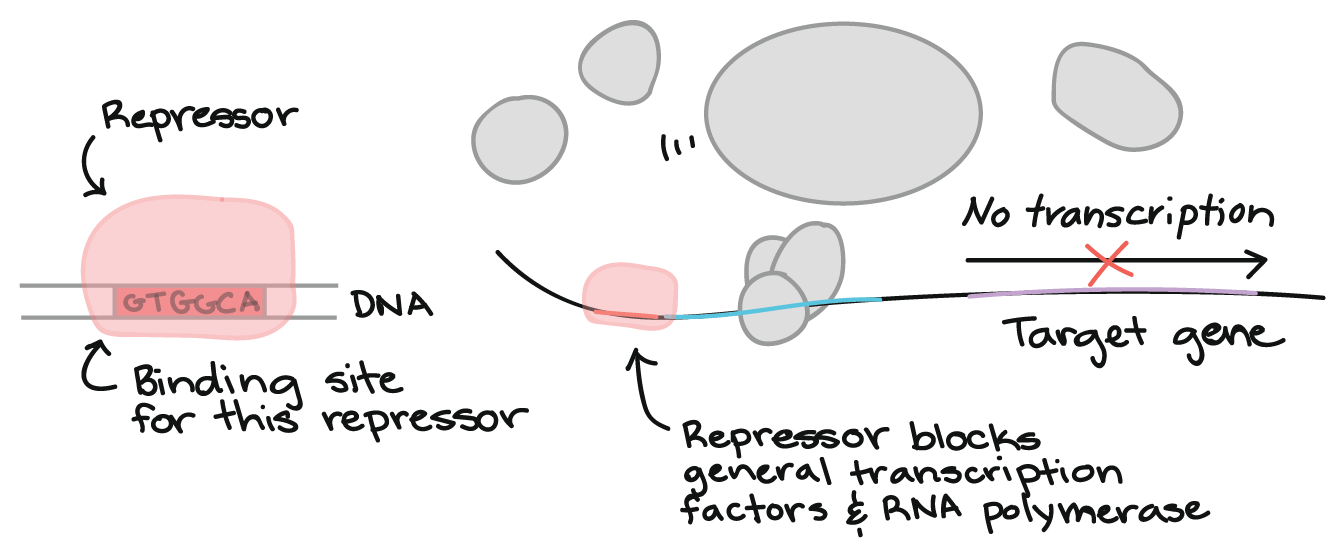
Several transcription factors are required for efficient transcription initiation in eukaryotes these factors help DNA polymerase to bind to the promoter region to form the pre-initiation complex at the TATA box. Initiation of transcription which results in the complex of proteins including the RNA polymerase enzyme and its various accessory proteins that will subsequently copy the gene into an RNA transcript being assembled upstream of the gene. Synthesis and processing of RNA.
Several initiation factors form a complex with the small 40S ribosomal subunit and. Formation of the transcription preinitiation complex PIC is nucleated by the TATA-binding protein TBP a subunit of TFIID that binds the TATA element and induces a. Activated transcription additionally depends on Mediator a 12 MDa multiprotein complex and the activity of a number of cofactors.
Eukaryotic transcription is carried out in the nucleus of the cell and proceeds in three sequential stages. 2015 to form a pre-initiation complex PIC on the promoter. Transcription factors that assist the binding of RNA polymerase II to the promoter and initiate low levels of transcription are called basal factors while other transcription factors are termed activators and repressors by binding.
Transcription factors are proteins that regulate the transcription of genesthat is their copying into RNA on the way to making a protein. One subunit of SL1 is the TATA-binding protein TBP. How do eukaryotic transcription factors help form the initiation complex.
Eukaryotic promoter regions contain a TATA box and a CAAT box. Before transcription can take place the DNA double helix must unwind near the gene that is getting transcribed. Two transcription factors UBF and SL1 bind cooperatively to the rDNA promoter and recruit RNA polymerase I to form an initiation complex.
RNA Polymerase II is the polymerase responsible for transcribing mRNA. Eukaryotes require transcription factors to first bind to the promoter region and then help recruit the appropriate polymerase. Canonical translation initiation is an intricate process that occurs through the necessary coordination of many translation initiation factors which work together to assemble the ribosomal subunits on the mRNA Translation initiation starts by the recognition of the 5 methylated cap structure of the mRNA by the cap-binding multiprotein.
They recruit RNA polymerase to the promoter In eukaryotes mRNAs have a modified guanosine covalently attached at the 5 end. The GTP necessary in the formation of the 5 cap on the transcript is modified by the addition of which of the following groups. The region of opened-up DNA is called a transcription bubble.
They recruit RNA polymerase to the promoter In transcription the DNA strand that. How do eukaryotic transcription factors help form the initiation complex-They synthesize the first 5-7 nucleotides of the mRNA-They recruit RNA polymerase to the promotor-They unwind the DNA helix at the promotor. TATA box is the site of the pre-initiation complex in.
How do eukaryotic transcription factors help form the initiation complex. They recruit RNA polymerase to the promoter. These general transcription factors include TFIIB TFIID TFIIE TFIIF and TFIIH.
The initiation complex moves the small ribosomal subunit through the 5 UTR scanning for the Kozak sequence 5 ACCAUG-3. These proteins help stabilize the formation of ribosomal preinitiation complexes around the start codon and are an important input for post-transcription gene regulation. Eukaryotic initiation factors are proteins or protein complexes involved in the initiation phase of eukaryotic translation.
The genes for tRNAs 5S rRNA and some of the small RNAs involved in splicing and protein transport are transcribed by polymerase III. So does the body of a bird tree or fungus. The initiation of mRNA synthesis requires Pol II and the general transcription factors TFIIA TFIIB TFIID TFIIE TFIIF and TFIIH Sainsbury et al.
-They recruit RNA polymerase to the promoter The GTP necessary in the formation of the 5 cap on the transcript is modified by the addition of which of the following groups. Transcription initiation is precisely controlled by the binding of a variety of trans-acting proteins termed transcription factors to the promoter and the enhancer. The General Transcription Factors locate the promoter then help RNA polymerase enter the complex to form the preinitiation complex.

Assembly Of Transcription Initiation Complexes In Human Mitochondria Download Scientific Diagram

0 Comments